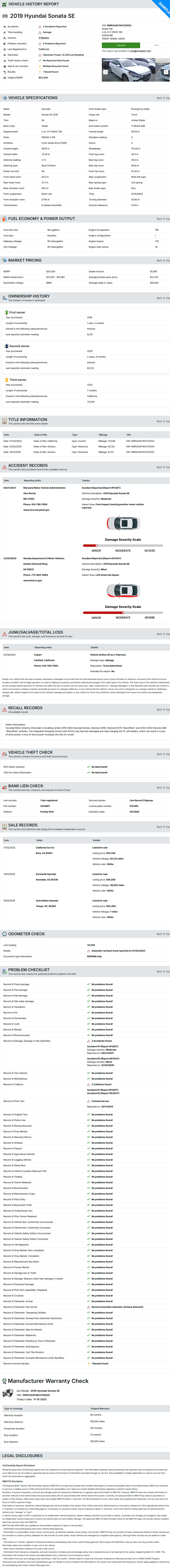
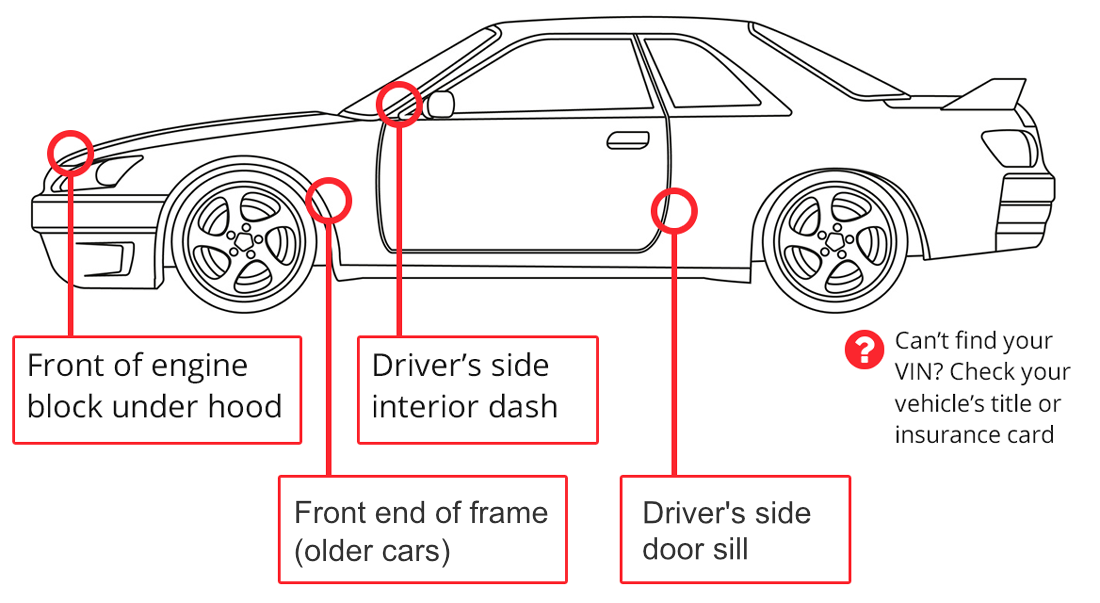
Performing a Vermont vehicle title search by VIN is one of the easiest ways to uncover a car’s complete background prior to making a pre-owned vehicle purchase. Start by locating the vehicle’s 17-digit VIN (Vehicle Identification Number). Once you have the number, you can enter it into an online Vermont vehicle title lookup tool. A VT car title search can instantly pull data from state and national databases, giving you access to essential details such as ownership history, title status, odometer readings and any existing liens.
Going beyond a basic Vermont title check, you can gain greater insight into the vehicle’s past by following it up with a comprehensive vehicle history report in Vermont. This report can help you spot red flags that may affect safety or resale value. By completing a thorough Vermont car title search, buyers can avoid hidden problems, verify the accuracy of the seller’s information and make more informed car-buying decisions.
Commonly used car pitfalls to look out for when buying a car in Vermont
- Unknowingly Buying a Salvage or Rebuilt Title Vehicle: A salvage branded title is an indicator that the vehicle was once declared a total loss by an insurance company due to major damage. The state of Vermont did not used to mandate that vehicles older than 15 years of age require a title for registration. Branded title reporting has been generally lax in the state, causing an influx of salvage title vehicles to flood the used car market.
- Unknowingly buying a history of a Water/Flood-Damaged Car: In recent years the state has experienced more frequent flooding events, causing significant damage to the car and other personal property. Flood-damage can cause serious issues on the vehicle’s electrical system, speed up corrosion, damage safety systems and more… Some of these flood-damaged vehicles will eventually make their way to the used car market and buying one of these vehicles can potentially lead to long-term electrical and mechanical problems.
- Buying a vehicle with an undisclosed lien: A lien is a debt incurred most commonly by the process of car financing through banks and other lenders. The lien will remain undischarged until such time as the debt, is paid in full. Buying a car with this type of issue could leave you responsible for someone else’s debt as the lender has an ownership claim on the vehicle and has the right to seize possession of it due to non-payment.
- Buying a Car with Odometer Discrepancies: Over 2 million vehicles registered in the country have a record of odometer tampering or mileage rollback. This is done by fraudsters to artificially inflate the vehicle’s value, leaving the buyer with a vehicle with decreased reliability and a higher cost of ownership.
- Buying a Car From a Seller Engaging in Title Jumping: Title jumping occurs when the seller transfers a vehicle without registering it in their name, which is illegal and may complicate ownership.
- Falling Victim to Legal Loopholes: For a long time, Vermont was one of the few states that allowed people to use a registration as a title for some older vehicles. This loophole was closed in 2023, but in its wake, it created a lot of vehicles with questionable origins.
- Buying a Car with Mismatched VIN: There are about 6 auto thefts reported for every 100,000 Vermont residents. Some of these stolen vehicles or vehicles brought in from out of state may be sold under false pretences with forged documents. This is why it is so important to verify the VIN displayed on the vehicle title actually matches with the VIN permanently imprinted on the vehicle itself. A car with a mismatched VIN can indicate theft, identity fraud, cloning or past alterations.
- Buying a Car with Incorrect or Missing Information: Errors in the title, such as misspelled names, wrong mileage, or incomplete details, can cause delays in registration or ownership transfer.